Ergonomics in digestive endoscopy: prevalence, types of musculoskeletal disorders and risk factors in endoscopists in Colombia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.829Keywords:
Ergonomics, Endosocpy, Injuries, Musculoskeletal, occupational healthAbstract
Introduction: The practice of digestive endoscopy is a physically demanding activity, with musculoskeletal disorders present in 39 % to 89 % of endoscopists, associated with “excessive use” maneuvers. Due to a lack of knowledge of this problem in endoscopists in Colombia, the main objective is to determine the prevalence, types, and risk factors of musculoskeletal disorders in specialists and graduate students. The secondary objective is to identify the occupational impact, treatments used, and importance of prevention and education in ergonomics.
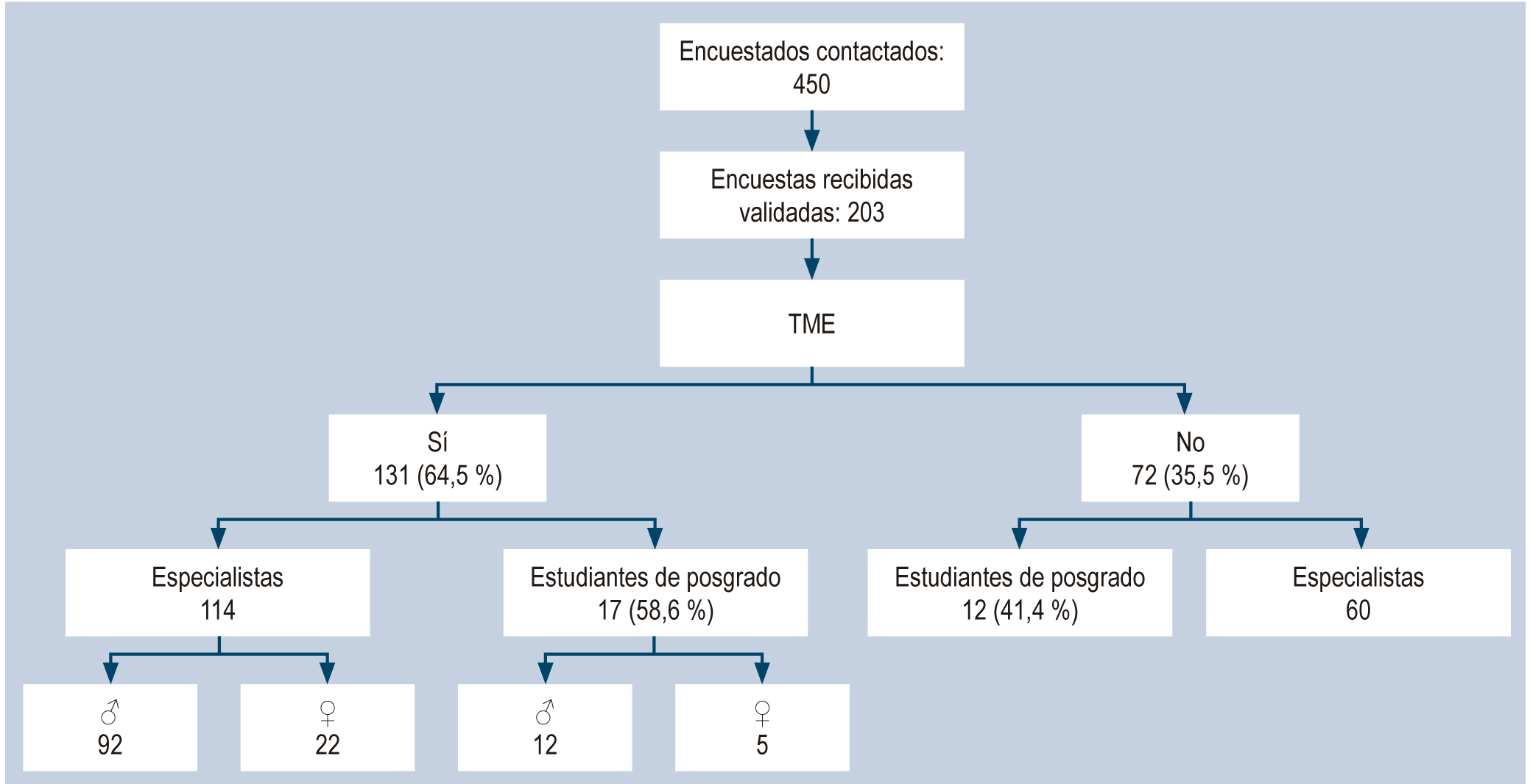
Materials and methods: Analytical cross-sectional observational study. Electronic survey methodology, open from June 1 to 30, 2021. Purposive sampling of 450 endoscopists from four scientific associations and eleven graduate programs, including 50 questions in six groups according to the objectives. We validated 203 responses, with 131 confirmations of musculoskeletal disorders, the group on which the analysis was performed.
Results: Global prevalence of musculoskeletal disorders of 64.5 % and prevalence in graduate students of 58.6 %. There was more significant involvement of the upper limbs (right shoulder, left thumb, right elbow), followed by lower back, neck, knees, and hips. Graduate students reported pain in the right hand/fingers (right thumb) and the lower back. There was no significant difference due to work factors, but there was a tendency for more reports when increasing the volume of procedures and years of professional practice. The labor impact showed 78 % absenteeism. The most used treatments were medication, physiotherapy, and rest; 93.8 % had not received ergonomic education. However, there is a positive perception (74.1 % to 90.9 %) of receiving formal training.
Discussion: The prevalence reflected the health and safety problem for the endoscopist. Demographic risk factors plus those of the endoscopic practice give rise to an individualized risk framework that enables endoscopists to understand learning and training as a way to prevent musculoskeletal disorders in themselves and their work team.
Downloads
References
Walsh CM, Qayed E, Aihara H, Anand GS, Byrne K, Chahal P, et al. Core curriculum for ergonomics in endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2021;93(6):1222-1227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2021.01.023
Yung DE, Banfi T, Ciuti G, Arezzo A, Dario P, Koulaouzidis A. Musculoskeletal injuries in gastrointestinal endoscopists: a systematic review. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Oct;11(10):939-947. https://doi.org/10.1080/17474124.2017.1356225
Austin K, Schoenberger H, Sesto M, Gaumnitz E, Teo Broman A, Saha S. Musculoskeletal Injuries Are Commonly Reported Among Gastroenterology Trainees: Results of a National Survey. Dig Dis Sci. 2019;64(6):1439-1447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-019-5463-7
Ridtitid W, Coté GA, Leung W, Buschbacher R, Lynch S, Fogel EL, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for musculoskeletal injuries related to endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;81(2):294-302.e4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2014.06.036
Hildebrandt VH, Bongers PM, van Dijk FJ, Kemper HC, Dul J. Dutch Musculoskeletal Questionnaire: description and basic qualities. Ergonomics. 2001;44(12):1038-55. https://doi.org/10.1080/00140130110087437
Matsuzaki I, Ebara T, Tsunemi M, Hatta Y, Yamamoto K, Baba A, et al. Effects of endoscopy-related procedure time on musculoskeletal disorders in Japanese endoscopists: a cross-sectional study. Endosc Int Open. 2021;9(5):E674-E683. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-1352-3850
Shergill AK, Asundi KR, Barr A, Shah JN, Ryan JC, McQuaid KR, et al. Pinch force and forearm-muscle load during routine colonoscopy: a pilot study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;69(1):142-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2008.09.030
Smith AC, Wolf JG, Xie GY, Smith MD. Musculoskeletal pain in cardiac ultrasonographers: results of a random survey. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 1997;10(4):357-62. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0894-7317(97)70073-7
van Det MJ, Meijerink WJ, Hoff C, Totté ER, Pierie JP. Optimal ergonomics for laparoscopic surgery in minimally invasive surgery suites: a review and guidelines. Surg Endosc. 2009;23(6):1279-85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-008-0148-x
Buschbacher R. Overuse syndromes among endoscopists. Endoscopy. 1994;26(6):539-44. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-1009030
Byun YH, Lee JH, Park MK, Song JH, Min BH, Chang DK, et al. Procedure-related musculoskeletal symptoms in gastrointestinal endoscopists in Korea. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14(27):4359-64. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.4359
Hansel SL, Crowell MD, Pardi DS, Bouras EP, DiBaise JK. Prevalence and impact of musculoskeletal injury among endoscopists: a controlled pilot study. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2009;43(5):399-404. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCG.0b013e31817b0124
Morais R, Vilas-Boas F, Pereira P, Lopes P, Simões C, Dantas E, et al. Prevalence, risk factors and global impact of musculoskeletal injuries among endoscopists: a nationwide European study. Endosc Int Open. 2020;8(4):E470-E480. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-1038-4343
Kamani L, Kalwar H. Ergonomic Injuries in Endoscopists and Their Risk Factors. Clin Endosc. 2021;54(3):356-362. https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2020.200
Villa E, Attar B, Trick W, Kotwal V. Endoscopy-related musculoskeletal injuries in gastroenterology fellows. Endosc Int Open. 2019;7(6):E808-E812. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-0811-5985
Campbell EV 3rd, Muniraj T, Aslanian HR, Laine L, Jamidar P. Musculoskeletal Pain Symptoms and Injuries Among Endoscopists Who Perform ERCP. Dig Dis Sci. 2021;66(1):56-62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-020-06163-z
Han S, Hammad HT, Wagh MS. High prevalence of musculoskeletal symptoms and injuries in third space endoscopists: an international multicenter survey. Endosc Int Open. 2020;8(10):E1481-E1486. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-1236-3379
Geraghty J, George R, Babbs C. A questionnaire study assessing overuse injuries in United Kingdom endoscopists and any effect from the introduction of the National Bowel Cancer Screening Program on these injuries. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;73(5):1069-70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2010.11.011
O’Sullivan S, Bridge G, Ponich T. Musculoskeletal injuries among ERCP endoscopists in Canada. Can J Gastroenterol. 2002;16(6):369-74. https://doi.org/10.1155/2002/523125
Al-Rifaie A, Gariballa M, Ghodeif A, Hodge S, Thoufeeq M, Donnelly M. Colonoscopy-related injury among colonoscopists: an international survey. Endosc Int Open. 2021;9(1):E102-E109. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-1311-0561
Roos KG, Marshall SW. Definition and usage of the term “overuse injury” in the US high school and collegiate sport epidemiology literature: a systematic review. Sports Med. 2014;44(3):405-21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-013-0124-z
Pawa S, Banerjee P, Kothari S, D’Souza SL, Martindale SL, Gaidos JKJ, et al. Are All Endoscopy-Related Musculoskeletal Injuries Created Equal? Results of a National Gender-Based Survey. Am J Gastroenterol. 2021;116(3):530-538. https://doi.org/10.14309/ajg.0000000000001136
Cohen DL, Naik JR, Tamariz LJ, Madanick RD. The perception of gastroenterology fellows towards the relationship between hand size and endoscopic training. Dig Dis Sci. 2008;53(7):1902-9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-007-0069-x
Markwell SA, Garman KS, Vance IL, Patel A, Teitelman M. Individualized ergonomic wellness approach for the practicing gastroenterologist (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2021 Aug;94(2):248-259.e2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2021.01.045
Nabi Z, Nageshwar Reddy D, Ramchandani M. Recent Advances in Third-Space Endoscopy. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2018;14(4):224-232.
Kuwabara T, Urabe Y, Hiyama T, Tanaka S, Shimomura T, Oko S, et al. Prevalence and impact of musculoskeletal pain in Japanese gastrointestinal endoscopists: a controlled study. World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17(11):1488-93. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i11.1488
Shergill AK, McQuaid KR, Rempel D. Ergonomics and GI endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;70(1):145-53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2008.12.235
Singla M, Kwok RM, Deriban G, Young PE. Training the Endo-Athlete: An Update in Ergonomics in Endoscopy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;16(7):1003-1006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2018.04.019
Stoner PL, Yang DJ, Rostom A, Draganov PV. Ergonomics in endoscopy: Can you teach an old dog new tricks? Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;92(2):456-457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2020.02.010
ASGE Technology Committee, Pedrosa MC, Farraye FA, Shergill AK, Banerjee S, Desilets D, Diehl DL, Kaul V, Kwon RS, Mamula P, Rodriguez SA, Varadarajulu S, Song LM, Tierney WM. Minimizing occupational hazards in endoscopy: personal protective equipment, radiation safety, and ergonomics. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;72(2):227-35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2010.01.071
Khan R, Scaffidi MA, Satchwell J, Gimpaya N, Lee W, Genis S, et al. Impact of a simulation-based ergonomics training curriculum on work-related musculoskeletal injury risk in colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;92(5):1070-1080.e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2020.03.3754
Shergill A, Harris Adamson C. Failure of an engineered sytem: The gastrointestinal endoscope. Tech Gastrointest Endosc. 2019;21(3):116-23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tgie.2019.02.001
Shergill AK, McQuaid KR. Ergonomic endoscopy: An oxymoron or realistic goal? Gastrointest Endosc. 2019;90(6):966-970. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2019.08.023
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Revista colombiana de Gastroenterología

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.


| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |














